BRABU BSc Chemistry New Syllabus 4-Year / 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th, 5th, 6th, 7th, 8th Semester Chemistry Syllabus: Babasaheb Bhimrao Ambedkar Bihar University is now starting CBCS based 4-Year Graduation Courses with many Social Science, Science, Commerce or Humanity Subjects.
Study Origin here prividing you BSc Chemistry Complete Syllabus for 1st Semester, 2nd Semester, 3rd Semester, 4th Semester, 5th Semester, 6th Semester, 7th Semester and 8th Semester Full Syllabus in PDF are Availble here.
BRABU BSc Chemistry Syllabus Type Availability:
- BRABU BSc Chemistry Major Core Courses (MJC) Syllabus
- BRABU BSc Chemistry Minor Courses (MIC) Syllabus
- BRABU BSc Chemistry Multidisciplinary Course Syllabus
- BRABU BSc Chemistry Ability Enhancement Course Syllabus
- BRABU BSc Chemistry Skill Enhancement Course Syllabus
- BRABU BSc Chemistry Value Added Course Syllabus
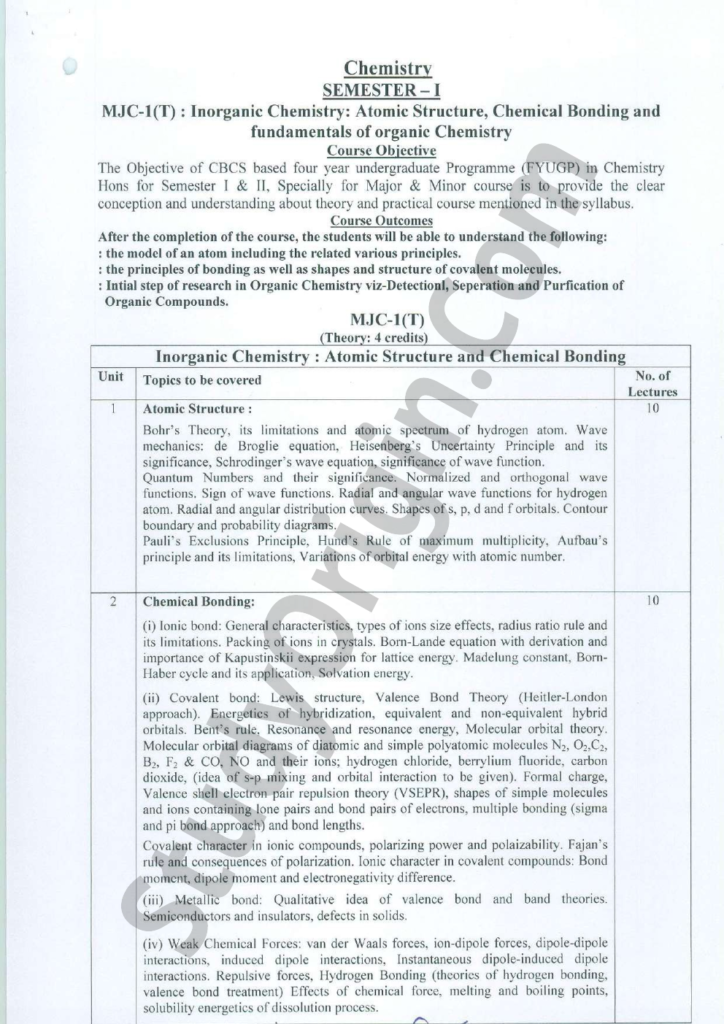
BSc Chemistry MJC-1 Syllabus (1st Semester)
Theory Paper Syllabus
| Unit | MJC -1: Inorganic Chemistry : Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding |
|---|---|
| 1 | Atomic Structure : Bohr’s Theory, its limitations and atomic speetrim, of hydrogen atom. Wave mechanics: de Broglie equation, Heisenbérg’s Uneertainty Principle and its significance, Schrodinger’s wave equation, significanee of wave function. Quantum Numbers and their significaneé» Normalized and orthogonal wave functions. Sign of wave functions. Radial and angular wave functions for hydrogen atom. Radial and angular distribution curves. Shapes offs, p, d and f orbitals. Contour boundary and probability diagrams. Pauli’s Exclusions Principle, Hund’s Rule of maximum multiplicity, Aufbau’s principle and its limitations, Variations of orbital energy with atomic number. |
| 2 | Chemical Bonding: (i) lonic bond: General characteristics, types of ions size effects, radius ratio rule and its limitations. Packing of.ions in crystals. Born-Lande equation with derivation and importance of Kapustinskii expression for lattice energy. Madelung constant, BornHaber cycle and its application, Solvation energy. (ii) Covalent bond: Lewis, structure, Valence Bond Theory (Heitler-London approach). Energetics Of hybridization, equivalent and non-equivalent hybrid orbitals. Bent’s Fule. Resonanee\and resonance energy, Molecular orbital theory. Molecular orbital diagrams of diatomic and simple polyatomic molecules N2, O2,C2, Bo, F> & CO, NO and their ions; hydrogen chloride, berrylium fluoride, carbon dioxide, (idea of S+p.mixing and orbital interaction to be given). Formal charge, Valence shellelectron pair repulsion theory (VSEPR), shapes of simple molecules and ions containing»lone pairs and bond pairs of electrons, multiple bonding (sigma and pi bond approach) and bond lengths. Covalent character in ionic compounds, polarizing power and polaizability. Fajan’s | rule and consequences of polarization. Ionic character in covalent compounds: Bond | oment, dipole moment and electronegativity difference. (iii) Metallic bond: Qualitative idea of valence bond and band _ theories. Semiconductors and insulators, defects in solids. (iv) Weak Chemical Forces: van der Waals forces, ion-dipole forces, dipole-dipole interactions, induced dipole interactions, Instantaneous dipole-induced dipole interactions. Repulsive forces, Hydrogen Bonding (theories of hydrogen bonding, valence bond treatment) Effects of chemical force, melting and boiling points, solubility energetics of dissolution process. |
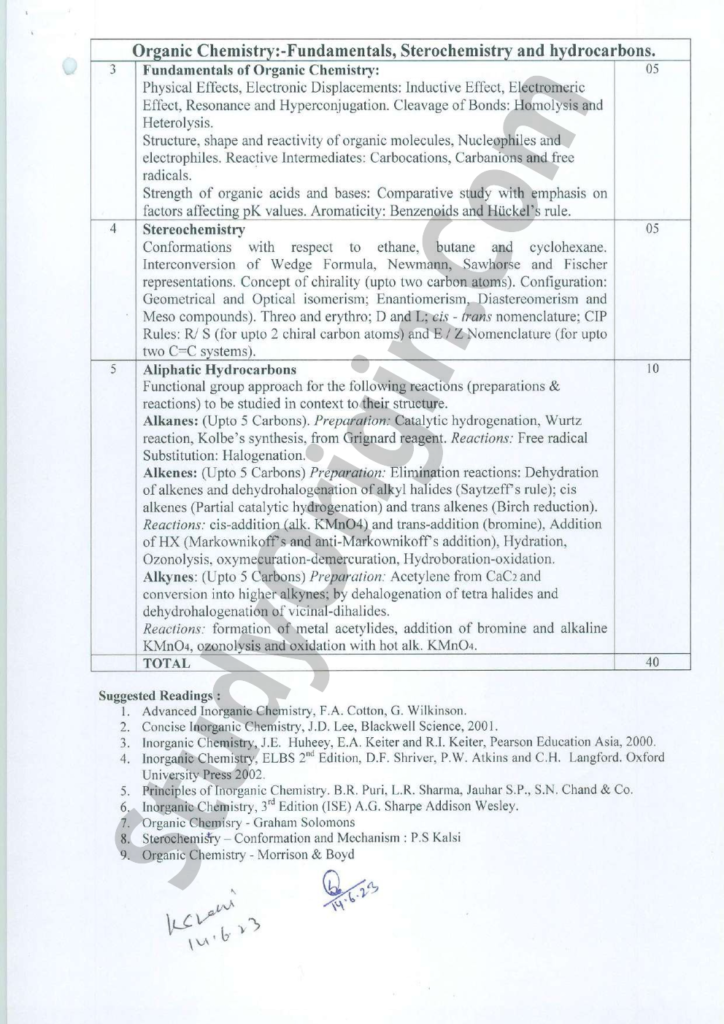
| 3 | Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry: Physical Effects, Electronic Displacements: Inductive Effect, Eléetromeric Effect, Resonance and Hyperconjugation. Cleavage of Bonds: Homolysis and Heterolysis. Structure, shape and reactivity of organic molecules, Nucleophiles and electrophiles. Reactive Intermediates: Carbocations, Carbanions and free radicals. Strength of organic acids and bases: Comparative study with emphasis on factors affecting pK values. Aromaticity: Benzenoids and Hiickel’s rule. |
| 4 | Stereochemistry: Conformations with respect to ethane, butane and cyclohexane. Interconversion of Wedge Formula, NewmannySawhorse and Fischer | representations. Concept of chirality (upto two carbon atoms). Configuration: Geometrical and Optical isomerism; Enantiomerism, Diastereomerism and Meso compounds). Threo and erythro; D and Lyeis – rans nomenclature; CIP Rules: R/ S (for upto 2 chiral carbon atoms) and E/ Z Nomenclature (for upto two C=C systems). |
| 5 | Aliphatic Hydrocarbons: Functional group approach for the followingeactions (preparations & reactions) to be studied in context to their structure. Alkanes: (Upto 5 Carbons). Preparation: Catalytic hydrogenation, Wurtz reaction, Kolbe’s synthesis, from Grignard reagent. Reactions: Free radical Substitution: Halogenation. Alkenes: (Upto 5 Carbons) Preparation: Elimination reactions: Dehydration of alkenes and dehydroh alogenation of alky! halides (Saytzeff’s rule); cis alkenes (Partial catalytic hydrogenation) and trans alkenes (Birch reduction). Reactions: cis-addition (alk. KMnO4) and trans-addition (bromine), Addition of HX (Markownikoff’s and anti-Markownikoff’s addition), Hydration, Ozonolysis, oxymecuration-demercuration, Hydroboration-oxidation. Alkynes: (Upto 5 Carbons) Preparation: Acetylene from CaC2 and conversion into higher alkynes; by dehalogenation of tetra halides and dehydrohalogenation ofvicinal-dihalides. Reactions: formation ofsmetal acetylide , addition of bromine and alkaline KMn04, ozonolysis atid oxidation with hot alk. KMnO4. |
MJC-1 Practical Paper Syllabus
| Practical- 1. Inorganic Chemisry Practical Acidimetry and Alkalimetry Preparation and dilution of standard soluti Permangnatometry / dichromatry lodometry / iodimetry | |
| Practical- 2. Organic Chemistry Practical Detection of elements, separation and p ion of Organic Compounds and Hydrolysis of ester. |

BSc Chemistry MIC-1 Syllabus (1st Semester)
Theory Paper Syllaubs
| Unit | MIC-1 Inorganic Chemistry Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding |
|---|---|
| 1 | Atomic Structure: Review of: Bohr’s theory and its limitations, dual behaviour of matter and radiation, de-Broglie’s relation, Heisenberg Uncertainty principle. Hydrogen atom spectra. Need of a new approach to Atomie structure. Significance of quantum numbers, orbital angular momentum and quantum numbers mi and ms. Shapes of s, p and d atomic orbitals, nodal planes. Discovery of spin, spin quantum number (s) and magnetic spin quantum number (ms). Rules for filling electrons in various orbitals, Electronic configurations of the atoms. Stability of half-filled and completely filled orbitals, concept of exchange energy. Relative energies of atomic orbitals, Anomalous electronic configuration, Hund’s, Pauli’s and Aufbau’s principle. |
| 2 | Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Ionic Bonding: General characteristics of ionic bonding Energy considerations in ionic bonding, lattice energy and solvation energy and their importance in the context of stability and solubility of ionic compounds. Statement of Born-Landé equation for calculation of lattice energy, Bornrules, Haber ionic cycle chara ter and its applications, in covalent polarizing compounds, power bond and moment, polarizability. dipole moment Fajan’s and percentage ionic character. Covalent bonding: VB Approach: Shapes of some inorganic molecules and ions on the basis of VSEPR and hybridization with suitable examples of linear, trigonal planar, square planar, tetrahedral, trigonal bipyramidal and octahedral arrangements. Concept of resonance and resonating structures in | various inorganic and organic compounds. |
| Section B: Organic Chemistry-1 (30 Periods) | |
| 3 | Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry Physical Effects, Electronic Displacements: Inductive Effect, Electromeric Effect, Resonance and Hyperconjugation. Cleavage of Bonds: Homolysis and Heterolysis. Structure, shape and reactivity of organic molecules: Nucleophiles and electrophiles. Reactive Intermediates: Carbocations, Carbanions and free radicals. Strength of organic acids and bases: Comparative study with emphasis on factors affecting pK values. Aromaticity: Benzenoids and Hiickel’s rule. |
| 4 | Stereochemistry Conformations with respect to ethane, butane and cyclohexane. Interconversion of Wedge Formula, Newmann, Sawhorse and Fischer representations. Concept of chirality (upto two carbon atoms). Configuration: Geometrical and Optical isomerism; Enantiomerism, Diastereomerism and Meso compounds). Threo and erythro; D and L; cis – ’ans nomenclature; CIP Rules: R/$ (for upto 2 chiral carbon atoms) and E / Z Nomenclature (for upto two C=C systems). |
Practical Paper Syllaubs
| Unit | MIC-1 Inorganic and Organic Chemistry Lab |
|---|---|
| 1 | Practical- 1, Inorganic Chemisry Practical a. Preparation and standardization of solutions. b. Permangnatometry / dichromatry, c. Acidimetry / Alkalimetry. |
| 2 | Practical- 2, Organic Chemisry Practical Organic Practical : Detection of elements, separation and purification of Organic Compounds. |
BSc Chemistry MDC-1 Syllabus (1st Semester)
Theory Paper Syllaubs
| Unit | MDC-1 Inorganic Chemistry Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding |
|---|---|
| 1 | Atomic Structure: Review of: Bohr’s theory and its limitations, dual behaviour of matter and radiation, de-Broglie’s relation, Heisenberg Uncertainty principle. Hydrogen atom spectra. Need of a new approach to Atomie structure. Significance of quantum numbers, orbital angular momentum and quantum numbers mi and ms. Shapes of s, p and d atomic orbitals, nodal planes. Discovery of spin, spin quantum number (s) and magnetic spin quantum number (ms). Rules for filling electrons in various orbitals, Electronic configurations of the atoms. Stability of half-filled and completely filled orbitals, concept of exchange energy. Relative energies of atomic orbitals, Anomalous electronic configuration, Hund’s, Pauli’s and Aufbau’s principle. |
| 2 | Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Ionic Bonding: General characteristics of ionic bonding Energy considerations in ionic bonding, lattice energy and solvation energy and their importance in the context of stability and solubility of ionic compounds. Statement of Born-Landé equation for calculation of lattice energy, Bornrules, Haber ionic cycle chara ter and its applications, in covalent polarizing compounds, power bond and moment, polarizability. dipole moment Fajan’s and percentage ionic character. Covalent bonding: VB Approach: Shapes of some inorganic molecules and ions on the basis of VSEPR and hybridization with suitable examples of linear, trigonal planar, square planar, tetrahedral, trigonal bipyramidal and octahedral arrangements. Concept of resonance and resonating structures in | various inorganic and organic compounds. |
| Section B: Organic Chemistry-1 (30 Periods) | |
| 3 | Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry Physical Effects, Electronic Displacements: Inductive Effect, Electromeric Effect, Resonance and Hyperconjugation. Cleavage of Bonds: Homolysis and Heterolysis. Structure, shape and reactivity of organic molecules: Nucleophiles and electrophiles. Reactive Intermediates: Carbocations, Carbanions and free radicals. Strength of organic acids and bases: Comparative study with emphasis on factors affecting pK values. Aromaticity: Benzenoids and Hiickel’s rule. |
| 4 | Stereochemistry Conformations with respect to ethane, butane and cyclohexane. Interconversion of Wedge Formula, Newmann, Sawhorse and Fischer representations. Concept of chirality (upto two carbon atoms). Configuration: Geometrical and Optical isomerism; Enantiomerism, Diastereomerism and Meso compounds). Threo and erythro; D and L; cis – ’ans nomenclature; CIP Rules: R/$ (for upto 2 chiral carbon atoms) and E / Z Nomenclature (for upto two C=C systems). |
Practical Paper Syllaubs
| Unit | MDC-1 Inorganic and Organic Chemistry Lab |
|---|---|
| 1 | Practical- 1, Inorganic Chemisry Practical a. Preparation and standardization of solutions. b. Permangnatometry / dichromatry, c. Acidimetry / Alkalimetry. |
| 2 | Practical- 2, Organic Chemisry Practical Organic Practical : Detection of elements, separation and purification of Organic Compounds. |
BRABU BSc Chemistry All Semester Syllabus Download Link:
| BSc Chemistry Semester-1 & 2 | Click Here |
| BSc Chemistry Semester-3 & 4 | जल्द ही आएगा |
| BSc Chemistry Semester-5 & 6 | जल्द ही आएगा |
| BSc Chemistry Semester-7 & 8 | जल्द ही आएगा |
BRABU BSc Chemistry (Semester-1 & 2) Syllabus PDF
[embeddoc url=”https://studyorigin.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/University-New-BSc-Chemistry-Syllabus-Sem-1-2.pdf”]BRABU BSc Chemistry Skill Enhancement Courses for Science
SEC-1 Subject List for 1st Semester
- Advance Spreadsheet Tools
- Basic IT Tolls
- Creative Writing
- Communication in Everyday life
SEC-2 Subject List for 2nd Semester
- Big Data Analysis
- Beginners Course to Calligraphy
- Intreduction to Cloud Computing (AWS)
- Personality Development & Communication
SEC-3 Subject List for 3rd Semester
- Prospecting E-waste for e Personal sustainability
- Visual Communication & Photography
- Graphic Design & Animation
- Statistics & Software Package
- Communication in Professional Life
BRABU BSc Chemistry Value Added Course List for Science
VAC-1 Subject List for 1st Semester
- Ayurveda & Nutrition
- Financial Literacy
- Ethic & Culture
- Art of Being Happy
- Swach Bharat
- Fit India
- Panchakosha: Holistic Development of Personality
- Culture & Communication
VAC-2 Subject List for 2nd Semester
- Vedic Mathematics
- Emotional Intelligence
- Yoga Philosophy & Practice
- Ethics & Values in Ancient indian Tradition
- Constitutional Values & Fundamental Duties
- Social & Emotional Leaming
- Ecology & Literature
BRABU BSc Chemistry Ability Enhancement Course List for Science
AEC-1 Subject List for 1st Semester
- MIL
AEC-2 Subject List for 2nd Semester
- Environmental Science
AEC-3 Subject List for 3rd Semester
- Coruse on Disaster Risk Management
AEC-4 Subject List for 4th Semester
- Course on NCC/NSS/NGO’s/Social Service/Scout & Guide/Sports.
How many Subjects are Available in BRABU BSc Chemistry Courese according to CBCS 4-Year Courses?
There are total 6 Subjects shoud be study to Complete their BSc Chemistry Courses
BRABU BSc Chemistry Major Core Courses (MJC) Syllabus
BRABU BSc Chemistry Minor Courses (MIC) Syllabus
BRABU BSc Chemistry Multidisciplinary Course Syllabus
BRABU BSc Chemistry Ability Enhancement Course Syllabus
BRABU BSc Chemistry Skill Enhancement Course Syllabus
BRABU BSc Chemistry Value Added Course Syllabus
How to Download BRABU BSc Chemistry Syllabus for All Semesters in PDF?
Steps to Download BRABU BSc Chemistry Syllabus are written following:
Visit www.studyorigin.com >>> फिर आपको मेनू पर Click करना है >>> अब University Wise Syllabus Button पर Click करना है >>> अब आपको University का नाम Select करना है >>> फिर आपको अपना Subject (Chemistry) पर Click करना है >>> तो आपका Syllaubs (Chemistry) वाला Article Open हो जाएगा
